EIGRP or Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol is a Cisco proprietary technology. However, it is still possible to integrate other routing protocols into EIGRP and/or vice versa. The most common thing to do in the network is injecting static route into EIGRP routing table so that hosts in the EIGRP network can communicate with the other hosts outside the EIGRP. Similar to OSPF, we can also Redistribute Static Route into EIGRP in Cisco IOS Router – except there's a little bit difference in the command used, which we will cover in this article.
- 1 255 Distance Metric For This Route Traveled
- 1 255 Distance Metric For This Route 46
- 1-255 Distance Metric For This Route
It can have the metric between 1 to 255. Please do rate for the helpful posts and mark correct answers. (ad=1 metric=0 1/0) for static routes and also standard mention that non valid metric is -1 and not 0. As clearly explained in this thread in Cisco IOS implementation static routes have an admin distance of 1 by default that can be. Router metrics are metrics used by a router to make routing decisions. A metric is typically one of many fields in a routing table.Router metrics help the router choose the best route among multiple feasible routes to a destination. The route will go in the direction of the gateway with the lowest metric. To understand the importance of routing metrics, consider the following example: Let's say that all routers are running RIP. R1 receives two possible routes to the 10.0.0.0/24 network; one going through R2, and one going through R3 and R4. Both routes are RIP routes and have the same administrative distance, so the metric is used to determine the best route. R1#show ip route 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 Routing entry for 4.4.4.4/32 Known via 'isis', distance 115, metric 30, type level-1 Redistributing via isis Last update from 192.168.12.2 on GigabitEthernet0/1, 00:00:10 ago Routing Descriptor Blocks:. 192.168.12.2, from 4.4.4.4, 00:00:10 ago, via GigabitEthernet0/1 Route metric is 30, traffic share.
How to Redistribute Static Route into EIGRP in Cisco IOS Router
Consider the following scenario where we will redistribute static route into EIGRP in Cisco IOS router.
In this scenario, R2 is the central router where it runs both EIGRP and static routes. R2 able to reach everyone in the topology, but both R1 and R4 cannot communicate with R3 in the EIGRP network and vice versa. It is required to modify the some of the configuration below and ensure all routers can communicate to each other.
Before we do any configuration, it is best to verify the issue by test pinging R1 and R4 from R3 and then display the existing entries in the routing table.
From the output above it can be understood that there is no routing entry to R1 and R4 in R3 routing table, therefore the ping failed. The problem can be solved by adding a static default route in R3 but it may not be the best solution because R3 already have EIGRP peering with R2, and R2 already have a specific static route to both R1 and R4. So instead of running a new routing protocol in R3, it is best just to redistribute the static route in R2 into EIGRP and with that way R3 will also obtain the route information to reach R1 and R4.
The command to redistribute staticroute into EIGRP in Cisco IOS router is:
Note that there are 5 metrics that must be specified when we redistribute static route into EIGRP in Cisco IOS router – and this applies when we redistribute other routing protocol into EIGRP as well. This because EIGRP is a smart routing protocol that consider all these aspects when creating a route entry. The mentioned metrics are:
- Bandwidth: Specify the bandwidth value of the link here in Kbits per second — this doesn't have to be the actual condition and it has nothing to do with the real bandwidth, as this is only for reference used by EIGRP to calculate the final metric.
- Delay: Specify the delay value here in 10 microseconds unit — again, this is only for reference used by EIGRP to calculate its metric.
- Reliability: Specify value here between 0-255 where 255 means EIGRP will see the link with maximum reliability
- Load: Specify value here between 1-255 where 255 means EIGRP will see the link as 100% loaded
- MTU: Specify the MTU value between 1-65535, normally it is 1500 but depending on the applications running in the network you might want to adjust this value. However, this does not change the actual MTU of the link.
Now, after understanding all the EIGRP metrics, here's the example of how to set the static route redistribution into EIGRP in R2:
Notice the change in R3 routing table after implementing the above command in R2:
R3 now have the route to R1 and R4 loopback address as an EIGRP external route, and ping to both address should now resulting in success.
Filtered Static Route Distribution into EIGRP using Route-Map
When a static route redistribution performed in Cisco IOS router, by default it will leak all the static routes information to the neighbor routing table. For some reason this can be unwanted or maybe it is not necessary to distribute all the static routes because only some specific routes are required to be distributed. In order to accommodate this kind of situation, we can control which static route to be distributed into other routing protocol by using route-map.
To create a route-map, first create an access-list which contains the network address that we are permitting to be distributed or denying all the address that we don't want to distribute. In this example, the access-list is created on R2 to only allow network address 4.4.4.4/32 and all other address will be denied by the implicit rule.
Next, we create the route-map which refers to the access-list that were created previously.
Lastly, go to EIGRP configuration and apply the redistribution command followed with reference to the route-map
The final EIGRP config on R2 will now look like this:
Notice that it is not required to re-specify the EIGRP metrics but the route-map command is automatically appended to the same redistribution command line we created before. And after implementing the command above, the route 1.1.1.1/32 should be removed from R3 routing table and leaving only 4.4.4.4/32 as we intended.
And that's how you Redistribute Static Route into EIGRP in Cisco IOS Router.
You may also like -
Arranda Saputra
- How to Move Documents Folder in Windows 10 - August 31, 2020
- How to Move Desktop Folder in Windows 10 - August 31, 2020
- Restore DHCP Server in Windows Server 2012 R2 - January 9, 2020
This tutorial explains IP route command and its parameter, argument and options in detail with examples. Learn how to configure default route and static route with IP route command in Cisco router step by step with practical example in packet tracer.
IP route command is used to configure the static route. Static routes are the most secure way of routing. They will also increase overall network performance. These features are extremely helpful in small network.
IP route command and parameters explained
We have two commands to configure the static route.
and
Let's explore above commands in detail
ip route
This is the base command which adds new route in routing table.
destination_network_#[subnet_mask]
This is the first parameter. It specifies the destination network address. We need to provide subnet mask if we are using sub-network. Sub-networks are the smaller networks created from one large network in subnetting. If we are not using sub-network then we can omit the subnet mask value. Scrutiny 8 2 0 – suite of web optimization tools. It will parse automatically.
IP_address_of_next_hop_neighbor / interface_to_exit
This parameter provides a way to reach the destination network. Both commands use separate way to assign this value. First command provides the IP address of next hop neighbor. It tells router that if it receives a packet for destination [that we set in previous parameter], forward that packet to this next hop neighbor IP address.
Second command also do the same job but in different way. It specifies exit interface instead of next hop IP address. It tells router that if it receives a packet for the destination specified by previous parameter then exits that packet from this interface. Device attached on other end of this interface will take care of the packet.
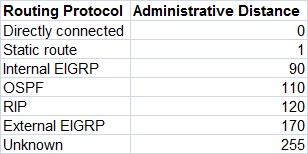
administrative_distance
Administrative distance is the trustworthiness of route. Route with the lowest AD value will be chosen while forwarding the packet. By default static route has two AD values depending on the previous parameter. If you have used next hop neighbor IP address, then the default AD value will be 1. If you have used exit interface, then the default AD value will be 0. This parameter allows us to create multiple static routes for the same destination. For example we can create primary and backup path for the destination network. To create backup path, we need to set AD value to higher than default, such as 2 or 3. With this configuration router will use primary path. Due to some reason if primary route fails, the router will start using backup route automatically.
permanent
When a route goes down router will remove that from routing table. Permanent parameter will keep this route in routing table even if it goes down. Its optional parameter we can omit it. If we omit it, router will remove this route from routing table if it goes down. You might use this parameter for security reason if you never want packets to take another path.
Configure Default Route
By default when a packet arrives in interface, router checks destination filed in packet and compare it with routing table. If it finds a match for destination network then it will forward that packet from related interface. If it does not find a match in routing table then it will discard that packet. This is the default behavior of router. Default route allows us to override this behavior. Default route is a way to deal with all unmatched packets. If no match for destination network found in routing table then it would be forwarded to the default route.
Following commands are used to set the default route
Or
Above command sets destination network to 0.0.0.0/0 that represents all networks.
IP route command example
For demonstration purpose we will use Packet Tracer network simulator software. Beside Packet Tracer you can use any other network simulator software such RouterSim, GNS, Boson or even better if you could afford, use real Cisco devices for follow this practice.
Create a practice topology as shown in fowling figure. Alternatively you can download this topology.
| Device | Connected from | Connected to | IP Address |
| PC0 | FastEthernet0 | Router0's FastEthernet0/0 | 10.0.0.2/8 |
| Router0 | FastEthernet0/0 | PC0's FastEthernet0 | 10.0.0.1/8 |
| Router0 | Serial 0/0/0 | Router1's serial0/0/0 | 192.168.0.253/30 |
| Router1 | Serial 0/0/0/ | Router0's serial0/0/0 | 192.168.0.254/30 |
| Router1 | FastEthernet0/0 | PC1's FastEthernet0 | 20.0.0.1/8 |
| PC1 | FastEthernet0 | Router1's FastEthernet0/0 | 20.0.0.2/8 |
Assign IP address to devices
Assign IP address 10.0.0.2/8 to PC0.
Repeat same process for PC1 and assign IP address 20.0.0.2/8.
Assign IP address to interfaces of router
Double click Router0 and click CLI and press Enter key to access command prompt of router.
Two interfaces FastEthernet0/0 and Serial0/0/0 of Router0 are used in this topology. By default interfaces on router are remain administratively down during the start up. We need to configure IP address and other parameters on interfaces before we could actually use them for routing. Interface mode is used to assign IP address and other parameters. Interface mode can be accessed from global configuration mode. Fuel for keynote themes 2 0. Following commands are used to access global configuration mode.
From global configuration mode we can enter in interface mode. From there we can configure the interface. Following commands will assign IP address on FastEthernet0/0.
interface fastEthernet 0/0 command is used to enter in interface mode.
ip address 10.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 command will assign IP address to interface.
no shutdown command will bring the interface up.
exit command is used to return in global configuration mode.
Serial interface needs two additional parameters clock rate and bandwidth. Every serial cable has two ends DTE and DCE. These parameters are always configured at DCE end. We can use show controllers interface command from privilege mode to check the cable's end.
Fourth line of output confirms that DCE end of serial cable is attached. If you see DTE here instead of DCE skip these parameters.
Now we have necessary information let's assign IP address to serial interface.
Router#configure terminal Command is used to enter in global configuration mode.
Router(config)#interface serial 0/0/0 Command is used to enter in interface mode.
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.0.253 255.255.255.252 Command assigns IP address to interface. For serial link we usually use IP address from /30 subnet.
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000 And Router(config-if)#bandwidth 64 In real life environment these parameters control the data flow between serial links and need to be set at service providers end. In lab environment we need not to worry about these values. We can use these values.
Router(config-if)#no shutdown Command brings interface up.
Router(config-if)#exit Command is used to return in global configuration mode.
We will use same commands to assign IP addresses on interfaces of Router1. Since we have provided clock rate and bandwidth on serial interface of Router0 we need not to assign them on serial interface of Router1. Following command will assign IP addresses on interface of Router1.
1 255 Distance Metric For This Route Traveled
Configure Static Route
Run following command from global configuration mode in routers.
Router0
Router1
1 255 Distance Metric For This Route 46
That's all we need to switch packet from one network to another. To verify the result we can use ping command. Access the command prompt of PC1 and use ping command to test the connectivity from PC0.
1-255 Distance Metric For This Route
A successful reply indicates that static routing is configured properly. In next article we will extend this example with more complex topology.

